There’s no question that digital marketing is highly competitive. To stay at the top of your game, you have to pull all the tools out of your toolbox, put them to work, and monitor them continually.
One of the metrics that can help you improve your overall results is CPM. Read on to gain a better understanding of what the CPM calculator is and how to calculate it, and how to use it to add value to your marketing campaigns.
What Is a CPM Calculator?
You’ll run across lots of acronyms in the digital world, so what exactly is CPM and why should you put in the effort to understand it? Let’s break its meaning down to the roots.
CPM stands for Cost per Mille. Mille is a French word that means thousand (fancy words we’re using here, in the PPC industry, young Padawan!). Essentially, in digital marketing, CPM refers to the cost per thousand impressions. In layman’s terms, the word “impressions” refers to the number of times someone sees an ad online. When you put it all together, CPM equates to the cost to have your ad published and viewed by 1,000 visitors.
With all that in mind, CPM is a metric you can use to monitor your ads’ performance. The next obvious question is how do you figure CPM? Is there a magical CPM calculator or something that can help you make quick sense out of this whole thing?
How Do You Calculate CPM? CPM Calculator Explained!
Yes, of course, there is a CPM calculator, and it’s very easy to use. All you have to do is to divide the total amount that you spend on a campaign by the number of impressions you receive. To get the CPM, multiply the result by 1,000. Ta-da!
In mathematical terms, the equation looks like this:

Now that you have the basic CPM calculator down, let’s dive into the issues that have an effect on CPM.
What Factors Affect CPM?
It might perk you up a bit to find that you have a low CPM rate. But before you get too excited, let’s take a look at the big picture.
Here’s a snapshot of 10 of the most common factors that have an effect on the CPM Calculator:
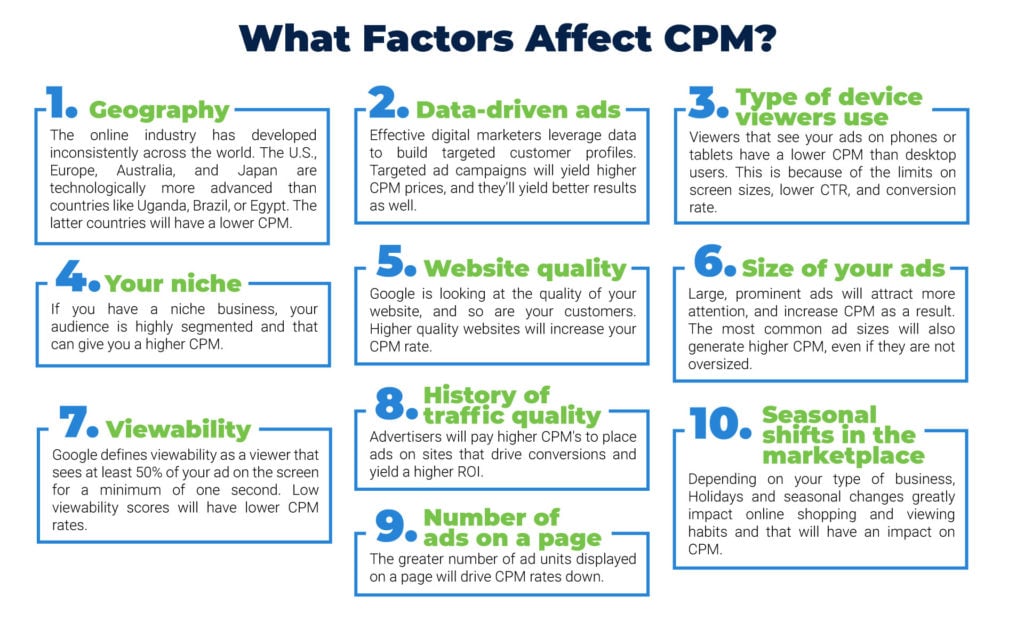
1. Geography-The online industry has developed inconsistently across the world. The U.S., Europe, Australia, and Japan are technologically more advanced than countries like Uganda, Brazil, or Egypt. The latter countries will have a lower CPM.
2. Data-driven ads-Effective digital marketers leverage data to build targeted customer profiles. Targeted ad campaigns will yield higher CPM prices, and they’ll yield better results as well.
3. Type of device viewers use-Viewers that see your ads on phones or tablets have a lower CPM than desktop users. This is because of the limits on screen sizes, lower CTR, and conversion rate.
4. Your niche-If you have a niche business, your audience is highly segmented and that can give you a higher CPM.
5. Website quality-Google is looking at the quality of your website, and so are your customers. Higher-quality websites will increase your CPM rate.
6. Size of your ads-Large, prominent ads will attract more attention, and increase CPM as a result. The most common ad sizes will also generate higher CPM, even if they are not oversized.
7. Viewability-Google defines viewability as a viewer that sees at least 50% of your ad on the screen for a minimum of one second. Low viewability scores will have lower CPM rates.
8. History of traffic quality-Advertisers will pay higher CPM’s to place ads on sites that drive conversions and yield a higher ROI.
9. Number of ads on a page-The greater number of ad units displayed on a page will drive CPM rates down.
10. Seasonal shifts in the marketplace-Depending on your type of business, Holidays and seasonal changes greatly impact online shopping and viewing habits and that will have an impact on CPM.
What Is a Good Price for CPM?
It all depends on what strategy you’re using and what is the goal of your campaign, therefore there’s no solid answer to what is a good price for CPM.
Let’s say for an example that you’re using contextual targeting – in those situations you might see CPM under $1.00. However, you will get a lot of impressions, but if you’re trying to reach engagement goals, then you might just figure out that’s not a good CPM because you will not be able to hit them.
So when it comes to the CPM’s, quality beats quantity. If you have expectations about how the campaign will output your outcome, using not always the cheapest strategy is not in your best interest.
What Are the Benchmarks for a Good CPM by Country and Industry?
Digital marketing metrics give you valuable data to enhance your ad campaigns but be careful not to make the mistake of relying too heavily on a few key metrics. The most effective strategies emerge when you consider the full scope of your data. To evaluate whether a CPM is good or bad, you have to give it the proper context.
Trends change within industries. The average CPM rates also fluctuate by country. On both accounts, by staying on top of global trends, you can use data to benchmark your results against CPM averages within a particular industry and the countries that the business works in to effectively evaluate the impact of CPM’s on ROI.
These statistics give you an idea of the average year-on-year decline of CPM rates in some of the major markets:
· Australia-CPM is down by 20%
· United States-CPM is down by 5%
· United Kingdom-CPM is down by 18%
CPM rates also vary by industry. Be aware that the rates can increase or decrease drastically month-over-month.
As you consider the many factors that affect CPM, it’s easier to see how these trends can change drastically in a short period of time.
Why Does CPM Change Seasonally?
Global and industry trends related to CPM or certainly something to pay attention to. It’s also wise to use a CPM calculator throughout the year and pay attention to cyclical patterns.
Here’s a list of factors that you may not have considered:

· Seasonal-As a business gears up for its highest-earning season, you’ll have a higher CPM.
· Holidays-From the holiday shopping season to holidays like Mother’s Day or Father’s Day, you can monitor CPMs to help you predict CPM rate and ROI.
· January doldrums-It’s common to see a drop in your CPM rate in January as holiday shoppers recoup from spending and make financial plans for the coming year.
· Fiscal year-Expect to see spikes in CPM as companies approach the end of their fiscal year, as they’ll be looking at unspent funds.
· Social and political issues-The recent global pandemic provides a bold example of how social or political issues have a vast impact on the global economy, and that impacts CPM as well.
There’s so much to learn about digital marketing! That’s what makes it such an exciting field to work in. The effort that you put into educating yourself about the best strategies can give you a big payoff. Be sure to visit the experts at ClickGUARD to learn more about PPC campaigns, click fraud, and how we can help you prevent click fraud.
Not that we’re bragging, but this really is the best click fraud protection software on all of the internet.
Conclusion and Summary
Calculating CPM is not a complicated process but it’s essential if you want to get the maximum out of your PPC Campaign.
There are multiple factors that affect CPM and you should always consider them when optimizing and creating strategies for the future.
CPM is known to change seasonally so always plan ahead.
Looking to learn more about Google Ads and how to improve the traffic you get from your Google paid campaigns? Check out our blog and follow us for more!



